The IELTS (International English Language Testing System) is a widely recognized English language proficiency exam. It assesses the language skills of non-native speakers of English who want to study or work in English-speaking countries. The IELTS consists of four sections: Listening, Reading, Writing, and Speaking. In this post, we’ll focus on the IELTS Listening Test and provide some tips and strategies to help you ace the exam.
What is the IELTS Listening Test?
The IELTS Listening Test is designed to assess your ability to understand spoken English in various contexts. The test consists of four sections, each with ten questions. You will hear four recordings, and you’ll have to answer the questions based on what you hear. The recordings include conversations, monologues, and discussions on academic and general topics.
Listening Test Tasks
Generally, the first part of IELTS is the Listening Test. This Part takes around 40 minutes and contains 40 questions in 4 Tasks. The test giver should hear these 4 parts for 30 minutes and then they have 10 minutes to write their answers on the answer sheet. Before starting this part of the listening test the test givers have some minutes time to read the questions. It is an important phase in the listening exam. So you should use it usefully.
Task one
In the first part of the listening test, the test givers should answer questions number 1 to question number 10. This part of the listening test is the easiest part. This part is an everyday conversation between two people. For instance a general conversation between two students on the university campus about general content.
Task two
This part is a monologue speak. It means one single person speaks about a general typic such as local facilities or a general condition. The second part of the listening test contains 10 questions (question number 11 to question number 20).
Task three
The third part of the test is a more complex conversation between up to four students in an academic position such as in a classroom during a lecture. The main content of their dialogue is a discussion in an academic environment. Then like in the other part, you answer 10 different types of questions (question number 21 to question number 30).
Task Four
In the last and most difficult part of the IELTS test, the test giver listens to a difficult academic monologue such as a professional presentation. The main content of this part is an academic subject. Then they should answer 10 difficult questions (question number 31 to question number 40).
IELTS Listening Mark Method
Each correct answer takes one point. In the IELTS the best brand score is 9 and the lowest brand score is 4. In the following table you can find and calculate your brand score:
| The number of Correct answers | Brand Score |
| 39-40 | 9 |
| 37-38 | 8.5 |
| 35-36 | 8 |
| 32-34 | 7.5 |
| 30-31 | 7 |
| 26-29 | 6.5 |
| 23-25 | 6 |
| 18-22 | 5.5 |
| 16-17 | 5 |
| 13-15 | 4.5 |
| 11-12 | 4 |
Question Types
The test giver should answer these 40 questions which could be in different types such as multiple-choice, matching, plan/map/diagram labelling, form/note/table/flow-chart/summary completion, and sentence completion.
Multiple Choice Questions
One of the most frequent types of questions in all parts of the IELTS test is Multiple choice. In this part, you should read the questions exactly. Because in some cases you should choices two correct answers. But in most Multiple choice questions, you must choose the best answer from 4 alternatives.
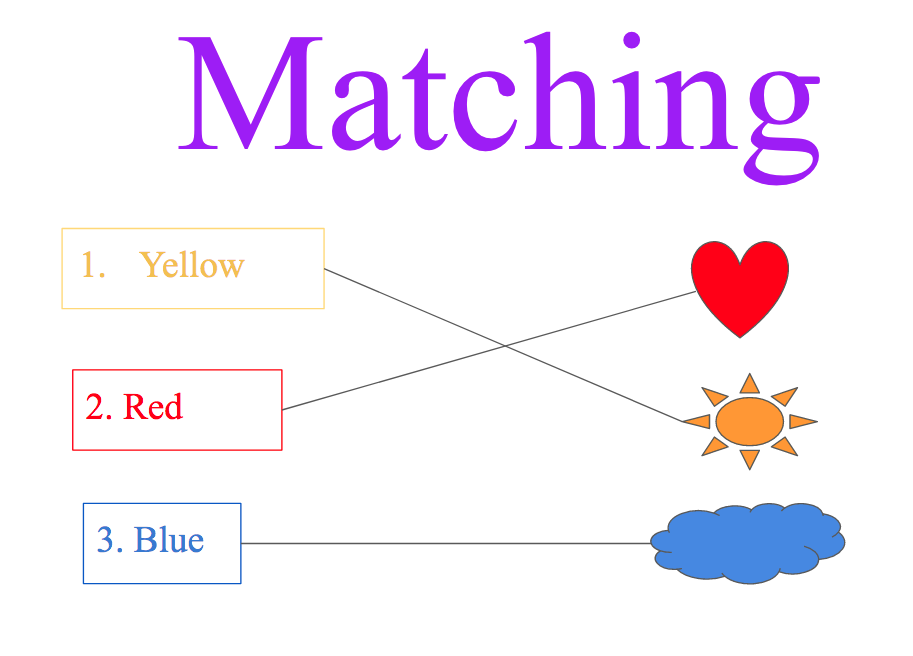
Matching Questions
The matching questions contain two items that should be matched. It means the test giver should pair items in one column with items in another column. Generally, the number of items in each column is equal.
Sentences, Form, Chart, and summary Completion Questions
In this part, the test giver should complete Sentences, Forms, charts, and summaries. It means there are some incomplete sentences that the test giver should complete.

Tips and Strategies for IELTS Listening Test
- Familiarize yourself with the test format
Before taking the IELTS Listening Test, make sure to familiarize yourself with the test format. This will help you understand what to expect and how to approach each section of the exam. You can find practice materials and sample tests online to help you prepare.
- Listen carefully
The key to doing well in the IELTS Listening Test is to listen carefully to the recordings. Focus on the speaker’s pronunciation, intonation, and stress. Pay attention to the context and try to understand the main ideas and details of what is being said.
- Use the time effectively
During the test, you’ll have some time to read the questions before listening to the recordings. Use this time effectively to read the questions carefully and underline keywords or phrases that will help you locate the answers in the recordings. Also, make sure to use the time given to check your answers after each section.
- Improve your vocabulary
Having a good vocabulary is crucial for doing well in the IELTS Listening Test. Make sure to practice new vocabulary regularly, and use it in different contexts to become familiar with its usage. You can find word lists and vocabulary exercises online to help you improve.
- Take notes
Taking notes can be helpful when trying to remember information from the recordings. Develop a shorthand system that works for you, and write down the key points and ideas as you listen. You can use your notes to answer the questions later.
- Practice, practice, practice
Practice is the key to success in the IELTS Listening Test. Take advantage of the many online resources available to practice listening to English in different contexts. You can also find practice tests to help you become more familiar with the format and types of questions.
In conclusion, the IELTS Listening Test can be challenging, but with the right strategies and preparation, you can improve your chances of doing well. Remember to listen carefully, use your time effectively, improve your vocabulary, take notes, and practice regularly. Good luck on your IELTS exam!
Would you like to know the salary amount of PhD and postdoc positions in Europe?
- Salary of PhD student and Postdoc in Denmark
- Salary of a PhD student and Postdoc in Norway
- Salary of PhD student and Postdoc in Switzerland
- Salary of PhD student and Postdoc in Sweden
- Salary of PhD student and Postdoc in Germany
- Salary of PhD and Postdoc in Ireland
- Salary of Postdocs in France
- Salary of PhD student and Postdoc in the UK
- Professors’ salary in the UK
- Salary of PhD student and Postdoc in the Netherlands
- Salary of PhD student and Postdoc in Finland
- Salary of PhD student and Postdoc in Austria
- Salary of Marie-curie postdoctoral fellowship
- Salary of PhD student in Marie-Curie ITN
- Doctorate Degree Business Administration Salary
You can find all the available full-funded PhD positions in different countries here.
- Germany – Fully Funded PhD
- Switzerland – Fully Funded PhD
- Denmark – Fully Funded PhD
- UK – Fully Funded PhD
- Sweden – Fully Funded PhD
- Finland – Fully Funded PhD
- Netherlands – Fully Funded PhD
- Norway – Fully Funded PhD
- Belgium – Fully Funded PhD
- Austria – Fully Funded PhD
- Australia – Fully Funded PhD
- France – Fully Funded PhD
- New Zealand – Fully Funded PhD
- Canada – Fully Funded PhD
- USA – Fully Funded PhD
- Luxembourg – Fully Funded PhD
- Spain – Fully Funded PhD
- Italy – Fully Funded PhD
- Iceland -Fully Funded PhD
